- Home
- Industrial Flanges
- Reducing Flange
Reducing Flange
Reducing Flange: Specifications | Materials | Types | Dimensions | Weight Chart | Tolerances | FAQ
High-quality ASME B16.5 Reducing Flanges manufactured and exported in carbon, stainless, alloy, and nickel alloys. Sizes range from ½” to 24” with pressure classes 150–2500. Shipped globally including Canada, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, and Italy.

Best Export Prices: sales@midlandforgefittings.com
Midland Forge and Fittings Pvt. Ltd, stands as a premier Manufacturer and Exporter of top-quality industrial reducing flanges. With extensive experience in the piping and engineering sector, we have established a strong reputation for reliability, precision, and compliance with international standards. we combine modern manufacturing processes with strict quality control measures to deliver products that meet the most demanding industrial requirements.
As a trusted industry partner, We specializes in reduing flanges made from carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, and high nickel alloys. Our focus on quality, efficiency, and on-time delivery has earned us long-term partnerships with clients across the globe.
A Reducing Flange is a specialized type of flange used to connect pipes of different diameters while maintaining a secure, leak-proof joint. Unlike standard flanges, reducing flanges allow a smooth transition from a larger pipe to a smaller one, ensuring efficient flow and minimal pressure drop. They are commonly manufactured in a range of materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, and high nickel alloys, to suit various industrial applications.
Reducing Flanges are widely used in industries such as oil & gas, petrochemical plants, power generation, water treatment, and industrial piping systems. They provide a reliable connection for high-pressure and high-temperature pipelines, reduce turbulence, and ensure long-lasting performance. Available in sizes from ½” to 24” and pressure classes from 150# to 2500#, these flanges are an essential component in critical piping networks worldwide.
Reducing Pipe Flange Specifications
Size Range
Pressure Rating - Class
Marking
Face Type / Flange Connection Type
Flange Form
Manufacturing Standards
Materials
Test Certificates
Dimensional Standards
Testing
Flange Coating/Surface Treatment
Production technique
Reducing Flange – Materials, Grades & Standards
| Material Category | Standards / Grades (ASTM / ASME) | Pressure Class / Size Range | Typical Use / Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | ASTM A182 F304 / F304L / F304H | Class 150 – 2500, Size ½”–48” | General purpose, corrosion-resistant piping |
| ASTM A182 F316 / F316L / F316H | Class 150 – 2500, Size ½”–48” | Chemical, marine, food & pharma industries | |
| ASTM A182 F321 / F321H | Class 150 – 1500, Size ½”–24” | High temperature, stabilized service | |
| Carbon Steel | ASTM A105 (Forged CS) | Class 150 – 2500, Size ½”–48” | Pressure piping, oil & gas, general industries |
| ASTM A350 LF2 (Low Temp CS) | Class 150 – 1500, Size ½”–24” | Cryogenic & low temperature applications | |
| Alloy Steel | ASTM A182 F11 / F22 (Cr-Mo) | Class 150 – 2500, Size ½”–24” | Power plants, refineries, steam pipelines |
| ASTM A182 F91 | Class 150 – 2500, Size ½”–24” | High-temperature, power generation | |
| Duplex / Super Duplex | ASTM A182 F51 / F53 / F55 / F60 (UNS S31803 / S32205 / S32750 / S32760) | Class 150 – 2500, Size ½”–24” | Offshore, seawater, high corrosion service |
| Nickel Alloys | ASTM B564 Inconel 600 / 625 / 718 | Class 150 – 2500, Size ½”–24” | Heat exchangers, chemical, aerospace |
| ASTM B564 Monel 400 / K500 | Class 150 – 2500, Size ½”–24” | Marine, seawater handling, pumps | |
| Copper Nickel | ASTM B151 / B467 (Cu-Ni 90/10, 70/30) | Class 150 – 600, Size ½”–24” | Shipbuilding, desalination, seawater systems |
| Titanium | ASTM B381 Gr. 2 / Gr. 5 | Class 150 – 600, Size ½”–12” | Aerospace, seawater, lightweight piping |
| Aluminium | ASTM B247 6061 / 5083 | Class 150 – 300, Size ½”–12” | Lightweight, non-corrosive, low-pressure piping |
Explore Industrial Flanges
- Flanges
- Slip On Flange
- Weld Neck Flange
- Socket Weld Flange
- Threaded Flange
- Lap Joint Flange
- Blind Flange
- Long Weld Neck Flange
- Reducing Flange
- Ring Type Joint (RTJ) Flange
- Plate Flange
- ASME B16.36 Orifice Flange
- Tongue and Groove Flange
- Male and Female Flange
- ASME B16.48 Spectacle Blind / Figure 8 Blank Flange
- Weldoflange
- Nipoflange
- Sweldolet Flange
Request for an Immediate Offer?
We will reply you in 2 hours during support time!
Conctact Now!Explore All Products
ANSI/ASME B16.5 Class 150 Reducing Flange – Dimensions & Sizes in mm
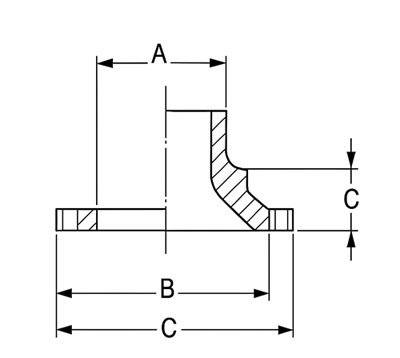
| NPS | DIAMETER | THICKNESS | DIA. | WELDING | MIN. | MIN. | MIN. | NECK | WELDING | JOINT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DN | O | T | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | |||
| 1/2 | 5.25 | 1.19 | 1.38 | 0.88 | .90 | 0.93 | 2.88 | 1.56 | 1.56 | ||||
| 15 | 133 | 30.5 | 34.9 | 22.2 | 22.9 | 23.5 | 73.0 | 40 | 40 | ||||
| 3/4 | 5.50 | 1.25 | 1.69 | 1.09 | 1.11 | 1.14 | 3.12 | 1.69 | 1.69 | ||||
| 20 | 140 | 32.0 | 42.9 | 27.8 | 28.2 | 29.0 | 79.4 | 43 | 43 | ||||
| 1 | 6.25 | 1.38 | 2.00 | 1.36 | 1.38 | 1.41 | 3.50 | 1.88 | 1.88 | ||||
| 25 | 159 | 35.0 | 50.8 | 34.5 | 34.9 | 36.0 | 88.9 | 48 | 48 | ||||
| 1 1/4 | 7.25 | 1.50 | 2.50 | 1.70 | 1.72 | 1.75 | 3.75 | 2.06 | 2.06 | ||||
| 32 | 184 | 38.5 | 63.5 | 43.3 | 43.7 | 44.5 | 95.2 | 52 | 52 | ||||
| 1 1/2 | 8.00 | 1.75 | 2.88 | 1.95 | 1.97 | 1.99 | 4.38 | 2.38 | 2.38 | ||||
| 40 | 203 | 44.5 | 73.0 | 49.6 | 50.0 | 50.5 | 111.4 | 60 | 60 | ||||
| 2 | 9.25 | 2.00 | 3.62 | To be | 2.44 | 2.46 | 2.50 | 5.00 | 2.75 | 2.75 | |||
| 50 | 235 | 51.0 | 92.1 | 61.9 | 62.5 | 63.5 | 127.0 | 70 | 70 | ||||
| 2 1/2 | 10.50 | 2.25 | 4.12 | specified | 2.94 | 2.97 | 3.00 | 5.62 | 3.12 | 3.12 | |||
| 65 | 267 | 57.5 | 104.8 | 74.6 | 75.4 | 76 | 142.9 | 79 | 79 | ||||
| 3 | 12.00 | 2.62 | 5.00 | by | 3.57 | 3.60 | 3.63 | 6.62 | 3.62 | 3.62 | |||
| 80 | 305 | 67.0 | 127.0 | 90.7 | 91.4 | 92 | 168.2 | 92 | 92 | ||||
| 4 | 14.00 | 3.00 | 6.19 | purchaser | 4.57 | 4.60 | 4.63 | 7.50 | 4.25 | 4.25 | |||
| 100 | 356 | 76.5 | 157.2 | 116.1 | 116.8 | 118 | 190.5 | 108 | 108 | ||||
| 5 | 16.50 | 3.62 | 7.31 | 5.66 | 5.69 | 5.69 | 9.00 | 5.12 | 5.12 | ||||
| 125 | 419 | 92.5 | 185.7 | 143.7 | 144.5 | 145 | 228.6 | 130 | 130 | ||||
| 6 | 19.00 | 4.25 | 8.50 | 6.72 | 6.75 | 6.75 | 10.75 | 6.0 | 6.0 | ||||
| 150 | 483 | 108.0 | 215.9 | 170.7 | 171.4 | 171 | 273.0 | 152 | 152 | ||||
| 8 | 21.75 | 5.00 | 10.62 | 8.72 | 8.75 | 8.75 | 12.50 | 7.0 | 7.0 | ||||
| 200 | 552 | 127.0 | 269.9 | 221.5 | 222.2 | 222 | 317.5 | 178 | 178 | ||||
| 10 | 26.50 | 6.50 | 12.75 | 10.88 | 10.92 | 10.88 | 16.50 | 9.0 | 9.0 | ||||
| 250 | 675 | 165.5 | 323.8 | 276.2 | 277.4 | 276 | 419.4 | 229 | 229 | ||||
| 12 | 30.00 | 7.25 | 15.00 | 12.88 | 12.92 | 12.94 | 18.25 | 10.0 | 10.0 | ||||
| 300 | 760 | 184.5 | 381.0 | 327.0 | 328.2 | 329 | 463.6 | 254 | 254 | ||||
Reducing Piping Flange Weight Chart (lbs) – Pressure Class 150 to 2500
| Nominal Pipe Size (Large Bore × Small Bore) | Class 150 (lbs) | Class 300 (lbs) | Class 600 (lbs) | Class 900 (lbs) | Class 1500 (lbs) | Class 2500 (lbs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2″ × 1″ | 9 | 14 | 21 | 28 | 36 | 55 |
| 3″ × 2″ | 16 | 25 | 40 | 55 | 78 | 110 |
| 4″ × 2″ | 22 | 34 | 55 | 75 | 105 | 150 |
| 6″ × 4″ | 38 | 58 | 95 | 135 | 190 | 280 |
| 8″ × 6″ | 61 | 92 | 155 | 220 | 315 | 470 |
| 10″ × 8″ | 95 | 145 | 240 | 345 | 500 | 740 |
| 12″ × 10″ | 135 | 210 | 355 | 510 | 740 | 1100 |
| 14″ × 12″ | 170 | 265 | 455 | 670 | 960 | 1450 |
| 16″ × 14″ | 210 | 325 | 560 | 830 | 1200 | 1800 |
| 18″ × 16″ | 260 | 400 | 695 | 1025 | 1500 | 2250 |
| 20″ × 18″ | 320 | 480 | 830 | 1220 | 1780 | 2680 |
| 24″ × 20″ | 420 | 640 | 1100 | 1600 | 2350 | 3550 |
Reducing Flange Tolerances as per ANSI / ASME B16.5, 16.47
| Parameter | Tolerance |
|---|---|
| Outside Diameter of Flange (D) | ± 1.5 mm (for sizes ≤ 24″) / ± 3.0 mm (for sizes > 24″) |
| Bolt Circle Diameter (K) | ± 1.5 mm |
| Bolt Hole Diameter (L) | +1.5 mm / 0 |
| Bolt Hole Spacing | ± 1.0 mm |
| Flange Thickness (B) | ± 1.5 mm (for thickness ≤ 25 mm) / ± 2.0 mm (for thickness > 25 mm) |
| Raised Face Diameter (G) | ± 1.5 mm |
| Hub Diameter at Base (A) | ± 1.5 mm |
| Bore Diameter (ID) | +1.0 mm / 0 |
| Concentricity of Bore to OD | ≤ 1.5 mm |
| Facing Runout (Raised Face/RTJ) | 0.5 mm max for ≤ 24″ / 1.0 mm max for > 24″ |
| Straightness of Hub | 0.5 mm max per 25 mm length |
| Bolt Hole Alignment (Rotational) | ± 0.8 mm at bolt circle |
| Spot Facing / Back Facing Depth | +1.5 mm / 0 |
What is a Reducing Flange?
A Reducing Flange is a type of flange that allows the connection of pipes with different diameters while maintaining a secure and leak-proof joint. Instead of using separate reducers and flanges, a reducing flange combines both functions into one component.
Key Points:
- Connects a larger pipe to a smaller one.
- Available in standards like ASME B16.5 and ASME B16.47.
- Manufactured in materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, and high nickel alloys.
- Designed to handle pressure classes 150# to 2500#.
This makes reducing flanges highly efficient, cost-effective, and widely used in critical piping systems.
What are the advantages of using Reducing Flanges?
Reducing flanges offer several benefits compared to using separate reducers and flanges.
- Space-Saving Design: Combines reducer and flange into one, saving installation space.
- Leak-Proof Connection: Provides a tighter seal compared to using two components.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces the need for additional fittings, lowering material and labor costs.
- Durability: Designed for high pressure and temperature applications.
- Versatility: Suitable for different industries due to availability in multiple materials and standards.
- Easy Installation: Simplifies assembly and reduces welding requirements.
How to select the right Reducing Flange for your application?
Choosing the correct reducing flange depends on several factors:
- Pipe Size & Reduction Ratio – Match the large and small bore sizes accurately.
- Pressure Class – Ensure the flange can handle the operating pressure.
- Material Selection – Choose based on fluid type (e.g., stainless steel for corrosive media).
- Temperature Range – Verify the material’s resistance to high or low temperatures.
- Industry Standards – Always check compatibility with ASME, ANSI, or other required codes.
- End Connection Type – Raised Face (RF), RTJ, or Flat Face depending on gasket use.
