- Home
- Industrial Flanges
- Plate Flange
Plate Flange
Plate Flange: Specifications | Materials | Types | Dimensions | Weight Chart | Tolerances | FAQ
Reliable ASME B16.5 Loose Plate Flanges – Exported in Carbon, Stainless, Alloy, and Nickel Alloys for Sizes ½”–24” and Classes 150–2500#. Global Delivery to Countries like Spain, Turkey, UAE, and Canada.

Best Export Prices: sales@midlandforgefittings.com
Midland Forge and Fittings Pvt. Ltd, is a leading manufacturer and exporter of high-quality plate flanges, renowned for precision, durability, and reliability. With extensive experience in the piping and industrial sector, the company delivers products that meet international standards, catering to diverse industries such as oil & gas, petrochemical, power generation, and water treatment. Our commitment to innovation, quality, and customer satisfaction has made us a trusted partner for clients across the globe.
we follow a structured and transparent working model to ensure efficiency and quality at every stage of production. Our policies emphasize strict quality control, timely delivery, and adherence to ASME and international standards. The company integrates advanced manufacturing technologies with skilled engineering teams, maintaining consistent product reliability and operational excellence. Customer-focused policies, including flexible order handling, global shipping, and responsive support, ensure that client requirements are met with professionalism and precision.
A plate flange is a type of industrial flange used to connect pipes, valves, pumps, and other equipment in a piping system. Manufactured as a solid circular plate with a central bore, it provides a strong and leak-proof connection between components. Plate flanges are designed to withstand high pressure and high temperature conditions and are often used in systems that require durability and reliable sealing. They are typically machined to meet ASME B16.5 standards, ensuring compatibility and safety in critical applications.
Plate flanges are available in carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, and nickel alloys, offering a wide range of material choices for various industrial needs. Known for their strength, corrosion resistance, and precision engineering, plate flanges provide secure, leak-proof connections in high-pressure piping systems. Their versatility and reliability make them a preferred choice for critical industrial applications worldwide.
Plate Pipe Flange Specifications
Size Range
Pressure Rating - Class
Marking
Face Type / Flange Connection Type
Flange Form
Manufacturing Standards
Materials
Test Certificates
Dimensional Standards
Testing
Flange Coating/Surface Treatment
Production technique
Plate Flange – Materials, Grades & Standards
| Material Category | Standards / Grades (ASTM / ASME) | Pressure Class / Size Range | Typical Use / Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | ASTM A182 F304 / F304L / F304H | Class 150 – 2500, Size ½”–48” | General purpose, corrosion-resistant piping |
| ASTM A182 F316 / F316L / F316H | Class 150 – 2500, Size ½”–48” | Chemical, marine, food & pharma industries | |
| ASTM A182 F321 / F321H | Class 150 – 1500, Size ½”–24” | High temperature, stabilized service | |
| Carbon Steel | ASTM A105 (Forged CS) | Class 150 – 2500, Size ½”–48” | Pressure piping, oil & gas, general industries |
| ASTM A350 LF2 (Low Temp CS) | Class 150 – 1500, Size ½”–24” | Cryogenic & low temperature applications | |
| Alloy Steel | ASTM A182 F11 / F22 (Cr-Mo) | Class 150 – 2500, Size ½”–24” | Power plants, refineries, steam pipelines |
| ASTM A182 F91 | Class 150 – 2500, Size ½”–24” | High-temperature, power generation | |
| Duplex / Super Duplex | ASTM A182 F51 / F53 / F55 / F60 (UNS S31803 / S32205 / S32750 / S32760) | Class 150 – 2500, Size ½”–24” | Offshore, seawater, high corrosion service |
| Nickel Alloys | ASTM B564 Inconel 600 / 625 / 718 | Class 150 – 2500, Size ½”–24” | Heat exchangers, chemical, aerospace |
| ASTM B564 Monel 400 / K500 | Class 150 – 2500, Size ½”–24” | Marine, seawater handling, pumps | |
| Copper Nickel | ASTM B151 / B467 (Cu-Ni 90/10, 70/30) | Class 150 – 600, Size ½”–24” | Shipbuilding, desalination, seawater systems |
| Titanium | ASTM B381 Gr. 2 / Gr. 5 | Class 150 – 600, Size ½”–12” | Aerospace, seawater, lightweight piping |
| Aluminium | ASTM B247 6061 / 5083 | Class 150 – 300, Size ½”–12” | Lightweight, non-corrosive, low-pressure piping |
Explore Industrial Flanges
- Flanges
- Slip On Flange
- Weld Neck Flange
- Socket Weld Flange
- Threaded Flange
- Lap Joint Flange
- Blind Flange
- Long Weld Neck Flange
- Reducing Flange
- Ring Type Joint (RTJ) Flange
- Plate Flange
- ASME B16.36 Orifice Flange
- Tongue and Groove Flange
- Male and Female Flange
- ASME B16.48 Spectacle Blind / Figure 8 Blank Flange
- Weldoflange
- Nipoflange
- Sweldolet Flange
Request for an Immediate Offer?
We will reply you in 2 hours during support time!
Conctact Now!Explore All Products
ANSI/ASME B16.5 Class 150 Plate Flange – Dimensions & Sizes in mm
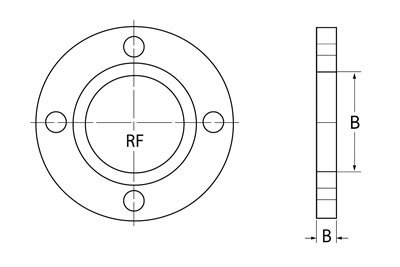
| Nominal Pipe Size (in) | OD of Flange (D) mm | Thickness (B) mm | RF Dia (G) mm | No. of Bolts (N) | Bolt Hole Dia (L) mm | Bolt Circle Dia (K) mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2″ | 110 | 16 | 70 | 4 | 18 | 85 |
| 3/4″ | 125 | 16 | 85 | 4 | 18 | 100 |
| 1″ | 140 | 18 | 100 | 4 | 18 | 115 |
| 1 1/2″ | 165 | 18 | 125 | 4 | 18 | 140 |
| 2″ | 185 | 20 | 150 | 4 | 18 | 160 |
| 3″ | 240 | 22 | 190 | 8 | 22 | 210 |
| 4″ | 295 | 22 | 250 | 8 | 22 | 265 |
| 6″ | 355 | 24 | 310 | 8 | 22 | 325 |
| 8″ | 405 | 26 | 370 | 8 | 26 | 380 |
| 10″ | 480 | 28 | 440 | 12 | 26 | 450 |
| 12″ | 560 | 30 | 500 | 12 | 26 | 530 |
ANSI/ASME B16.5 Class 300 Plate Flange – Dimensions & Sizes in mm
| Nominal Pipe Size (in) |
OD of Flange (D) mm |
Thickness (B) mm |
RF Dia (G) mm |
No. of Bolts (N) |
Bolt Hole Dia (L) mm |
Bolt Circle Dia (K) mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2″ | 120 | 19 | 70 | 4 | 19 | 90 |
| 3/4″ | 135 | 19 | 85 | 4 | 19 | 105 |
| 1″ | 150 | 22 | 100 | 4 | 19 | 120 |
| 1 1/2″ | 180 | 22 | 125 | 4 | 19 | 145 |
| 2″ | 200 | 24 | 150 | 4 | 19 | 165 |
| 3″ | 250 | 26 | 190 | 8 | 22 | 225 |
| 4″ | 310 | 28 | 250 | 8 | 22 | 285 |
| 6″ | 375 | 32 | 310 | 8 | 22 | 345 |
| 8″ | 445 | 34 | 370 | 8 | 26 | 410 |
| 10″ | 520 | 38 | 440 | 12 | 26 | 480 |
| 12″ | 600 | 40 | 500 | 12 | 26 | 560 |
ANSI/ASME B16.5 Class 400 Plate Flange – Dimensions & Sizes in mm
| Nominal Pipe Size (in) |
OD of Flange (D) mm |
Thickness (B) mm |
RF Dia (G) mm |
No. of Bolts (N) |
Bolt Hole Dia (L) mm |
Bolt Circle Dia (K) mm |
Approx Wt (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2″ | 125 | 22 | 70 | 4 | 19 | 95 | 3.5 |
| 3/4″ | 140 | 22 | 85 | 4 | 19 | 110 | 4.2 |
| 1″ | 160 | 26 | 100 | 4 | 19 | 125 | 5.5 |
| 1 1/2″ | 185 | 26 | 125 | 4 | 22 | 150 | 7.0 |
| 2″ | 210 | 28 | 150 | 4 | 22 | 170 | 9.0 |
| 3″ | 260 | 32 | 190 | 8 | 22 | 235 | 17 |
| 4″ | 320 | 34 | 250 | 8 | 22 | 295 | 25 |
| 6″ | 385 | 38 | 310 | 8 | 26 | 355 | 38 |
| 8″ | 455 | 42 | 370 | 8 | 26 | 420 | 58 |
| 10″ | 530 | 46 | 440 | 12 | 26 | 490 | 90 |
| 12″ | 610 | 50 | 500 | 12 | 26 | 570 | 130 |
ANSI/ASME B16.5 Class 600 Plate Flange – Dimensions & Sizes in mm
| Nominal Pipe Size (in) |
OD of Flange (D) mm |
Thickness (B) mm |
RF Dia (G) mm |
No. of Bolts (N) |
Bolt Hole D ia (L) mm |
Bolt Circle Dia (K) mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2″ | 130 | 25 | 70 | 4 | 19 | 90 |
| 3/4″ | 145 | 25 | 85 | 4 | 19 | 105 |
| 1″ | 160 | 28 | 100 | 4 | 22 | 120 |
| 1 1/2″ | 190 | 30 | 125 | 4 | 22 | 145 |
| 2″ | 215 | 32 | 150 | 4 | 22 | 170 |
| 3″ | 270 | 38 | 190 | 8 | 26 | 225 |
| 4″ | 330 | 42 | 250 | 8 | 26 | 285 |
| 6″ | 395 | 48 | 310 | 8 | 26 | 355 |
| 8″ | 470 | 54 | 370 | 8 | 30 | 420 |
| 10″ | 545 | 60 | 440 | 12 | 30 | 490 |
| 12″ | 620 | 68 | 500 | 12 | 30 | 570 |
ANSI/ASME B16.5 Class 900 Plate Flange – Dimensions & Sizes in mm
| Nominal Pipe Size (in) |
OD of Flange (D) mm |
Thickness (B) mm |
RF Dia (G) mm |
No. of Bolts (N) |
Bolt Hole Dia (L) mm |
Bolt Circle Dia (K) mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2″ | 140 | 32 | 70 | 4 | 22 | 95 |
| 3/4″ | 155 | 32 | 85 | 4 | 22 | 110 |
| 1″ | 170 | 36 | 100 | 4 | 22 | 125 |
| 1 1/2″ | 200 | 40 | 125 | 4 | 26 | 150 |
| 2″ | 225 | 44 | 150 | 4 | 26 | 170 |
| 3″ | 280 | 50 | 190 | 8 | 26 | 225 |
| 4″ | 345 | 54 | 250 | 8 | 30 | 285 |
| 6″ | 410 | 60 | 310 | 8 | 30 | 355 |
| 8″ | 490 | 70 | 370 | 8 | 33 | 420 |
| 10″ | 565 | 78 | 440 | 12 | 33 | 490 |
| 12″ | 640 | 85 | 500 | 12 | 33 | 570 |
ANSI/ASME B16.5 Class 1500 Plate Flange – Dimensions & Sizes in mm
| Nominal Pipe Size (in) |
OD of Flange (D) mm |
Thickness (B) mm |
RF Dia (G) mm |
No. of Bolts (N) |
Bolt Hole Dia (L) mm |
Bolt Circle Dia (K) mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2″ | 160 | 50 | 70 | 4 | 26 | 95 |
| 3/4″ | 175 | 50 | 85 | 4 | 26 | 110 |
| 1″ | 190 | 55 | 100 | 4 | 26 | 125 |
| 1 1/2″ | 220 | 60 | 125 | 4 | 30 | 150 |
| 2″ | 245 | 65 | 150 | 4 | 30 | 170 |
| 3″ | 300 | 72 | 190 | 8 | 33 | 225 |
| 4″ | 365 | 78 | 250 | 8 | 33 | 285 |
| 6″ | 430 | 85 | 310 | 8 | 36 | 355 |
| 8″ | 515 | 95 | 370 | 8 | 36 | 420 |
| 10″ | 590 | 108 | 440 | 12 | 36 | 490 |
| 12″ | 665 | 120 | 500 | 12 | 36 | 570 |
ANSI/ASME B16.5 Class 2500 Plate Flange – Dimensions & Sizes in mm
| Nominal Pipe Size (in) |
OD of Flange (D) mm |
Thickness (B) mm |
RF Dia (G) mm |
No. of Bolts (N) |
Bolt Hole Dia (L) mm |
Bolt Circle Dia (K) mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2″ | 175 | 65 | 70 | 4 | 30 | 95 |
| 3/4″ | 190 | 65 | 85 | 4 | 30 | 110 |
| 1″ | 210 | 72 | 100 | 4 | 33 | 125 |
| 1 1/2″ | 240 | 78 | 125 | 4 | 33 | 150 |
| 2″ | 270 | 85 | 150 | 4 | 36 | 170 |
| 3″ | 330 | 95 | 190 | 8 | 36 | 225 |
| 4″ | 400 | 105 | 250 | 8 | 36 | 285 |
| 6″ | 470 | 120 | 310 | 8 | 36 | 355 |
| 8″ | 560 | 135 | 370 | 8 | 39 | 420 |
| 10″ | 640 | 150 | 440 | 12 | 39 | 490 |
| 12″ | 720 | 170 | 500 | 12 | 39 | 570 |
Plate Piping Flange Weight Chart (lbs) – Pressure Class 150 to 2500
| Nominal Pipe Size (in) | 150# | 300# | 400# | 600# | 900# | 1500# | 2500# |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2″ | 2.1 | 3.0 | 3.5 | 5.0 | 7.0 | 12 | 18 |
| 3/4″ | 2.5 | 3.6 | 4.2 | 5.8 | 8.0 | 14 | 21 |
| 1″ | 3.3 | 4.6 | 5.5 | 7.0 | 10 | 18 | 28 |
| 1 1/2″ | 4.5 | 6.2 | 7.0 | 9.5 | 13 | 24 | 38 |
| 2″ | 6.2 | 8.0 | 9.0 | 12 | 16 | 30 | 48 |
| 3″ | 12 | 15 | 17 | 24 | 32 | 55 | 85 |
| 4″ | 18 | 22 | 25 | 35 |
Plate Flange Tolerances as per ANSI / ASME B16.5, 16.47
| Parameter | Tolerance / Allowable Deviation | Notes / Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Outside Diameter (D) | ±1.5% of nominal OD | Applies to all classes 150#–2500# |
| Flange Thickness (B) | ±3 mm for sizes ≤ 6″; ±5 mm for sizes > 6″ | Based on class and flange schedule |
| Raised Face Diameter (G) | +0 / −1.0 mm | Ensures proper gasket seating |
| Raised Face Height | ±0.5 mm | For RF type flanges |
| Bolt Circle Diameter (K) | ±1.0 mm | Ensures proper bolt alignment |
| Number of Bolt Holes (N) | As per standard | No deviation allowed |
| Bolt Hole Diameter (L) | +0 / −0.5 mm | Ensures proper bolt fit |
| Hub Diameter (A) | ±1.0 mm | Applies to weld neck and plate flanges |
| Hub Length / Thickness (H) | ±2.0 mm | Applies to weld neck flanges |
| Flatness / Face Runout | 0.5 mm max for ≤12″; 1 mm max for >12″ | Ensures proper sealing |
| Bore Diameter (ID) | +0 / −0.5 mm | Applies for slip-on and weld neck flanges |
What exactly is a Plate Flange and how does it differ from other flanges?
-
A Plate Flange is a flat, circular disc with bolt holes, used to connect pipes, valves, equipment, or ducts.
-
Unlike Weld Neck or Slip-On Flanges, plate flanges do not have a hub, which reduces material use and weight.
-
The flat design makes it ideal for low to medium-pressure systems, low-temperature applications, and situations where welding is difficult or unnecessary.
-
Because of its simplicity, it is often used in temporary piping, tanks, and fabricated structures where cost-effectiveness and ease of installation are priorities.
-
Practical Difference: Weld Neck flanges provide better stress distribution, while Plate Flanges focus on space saving and economy.
What are the key design considerations for Plate Flanges?
Bolt Hole Pattern: Alignment with mating flange is crucial. Misalignment can lead to leaks, gasket blowouts, or bolt failure.
Raised Face (RF) vs Flat Face (FF):
RF Flanges: Ensure better gasket compression, preferred in medium-pressure systems.
FF Flanges: Used in low-pressure or non-gasketed systems, often where welding or bolting is simpler.
Pressure Rating: Must match the ASME class (150#–2500#); improper rating can lead to mechanical failure.
Flange Thickness: Must accommodate internal pressure, bending stress, and gasket type. Engineers often consult ASME B16.5 tables.
Corrosion Allowance: Extra thickness may be applied to account for corrosion over service life.
How is the weight of a Plate Flange calculated and why is it important?
Weight depends on nominal diameter, plate thickness, material density, and bolt hole pattern.
Plate Flanges are lighter than hubbed flanges, which makes handling, lifting, and installation easier.
Approximate weights are referenced from ASME B16.5/16.47 tables, but custom flanges may vary.
Weight is critical for:
Support structure design (prevent sagging).
Transportation and handling planning.
Safety during installation, especially for large diameters.
