- Home
- Forged Fittings
- Forged Insert
Forged Insert
Forged Insert : Specifications | Materials | Dimensions | Weight Chart | Tolerances | FAQ
Reliable Manufacturer & Supplier of ASME B16.11 Forged Socket Weld Reducer Insert – Sizes ½” to 4”, Class 2000#, 3000#, 6000#, and 9000#, Available in Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel & High Nickel Alloys for Global Markets (UK, Italy, Canada, Saudi Arabia, South Africa & UAE)

Best Export Prices: sales@midlandforgefittings.com
Midland Forge and Fittings Pvt. Ltd. is a trusted name in the manufacturing and supply of forged fittings, serving global industries with precision-engineered solutions. With a strong focus on quality, reliability, and innovation, we have established ourselves as a reliable partner for critical piping applications. Our manufacturing expertise, backed by advanced machinery and skilled professionals, ensures that every product meets international standards such as ASME, ASTM, and ANSI.
We believe in delivering more than just products – we deliver long-term solutions. Our company emphasizes strict quality control, timely delivery, and complete customer satisfaction.
A forged insert is a high-quality forged fitting designed to provide a smooth transition between different piping sizes in high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Unlike standard reducers, forged inserts are compact fittings that are commonly used in place of reducers for smaller bore piping systems, ensuring leak-proof connections and structural integrity. They are typically installed by socket weld or threaded connections, depending on system requirements.
forged inserts are available in pressure classes 2000#, 3000#, 6000#, and 9000# as per ASME B16.11 standards. The size range typically covers ½” to 4”, meeting a broad spectrum of piping requirements. With superior mechanical strength and precise tolerances, forged inserts provide excellent performance under corrosive and high-pressure service conditions, making them a preferred choice in demanding industrial applications.
Our presence extends across major global markets including the UK, Italy, Canada, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa. With a strong distribution network and the capacity to manufacture both standard and customized forged fittings, we cater to diverse project requirements. At Midland Forge, we are committed to providing world-class forged components that combine durability, precision, and cost-effectiveness.
Forged Insert Specifications
Size Range – (Socket weld & Screwed-Threaded)
Pressure Rating
Marking
Fitting Types
Thread/MTC
Manufacturing Standards
Materials
Dimensional Standards
Testing
Surface Finish
Threaded Insert – Materials, Grades & Standards
| Material Category | Grade | Standards (ASTM / ASME) | Typical Use / Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | 304 / 304L / 304H | ASTM A182 F304 / F304L / F304H | General purpose, corrosion resistance |
| 316 / 316L / 316H | ASTM A182 F316 / F316L / F316H | Marine, chemical, and food processing | |
| 317 / 317L | ASTM A182 F317 / F317L | High corrosion resistance | |
| 321 / 321H | ASTM A182 F321 / F321H | High temperature, stabilized service | |
| 347 / 347H | ASTM A182 F347 / F347H | High-temp, pressure systems | |
| 904L | ASTM A182 F904L | Acid handling, sulfuric environments | |
| 254 SMO | ASTM A182 F44 | High chloride & seawater applications | |
| Carbon Steel | A105 | ASTM A105 | Pressure piping & general industries |
| A350 LF2 | ASTM A350 LF2 | Low temperature services | |
| A694 F42 / F46 / F52 / F56 / F60 / F65 / F70 | ASTM A694 | High-pressure pipelines, oil & gas | |
| Alloy Steel | F1 / F5 / F9 | ASTM A182 F1 / F5 / F9 | High-temp & pressure pipelines |
| F11 / F22 | ASTM A182 F11 / F22 | Steam lines & refineries | |
| F91 | ASTM A182 F91 | Power generation, high performance | |
| Duplex Steel | UNS S31803 / S32205 | ASTM A182 F51 / F60 | Corrosion resistance, high strength |
| Super Duplex Steel | UNS S32750 / S32760 | ASTM A182 F53 / F55 | Offshore, seawater applications |
| Nickel Alloys | Nickel 200 / 201 | ASTM B564 | Alkali & chemical processing |
| Inconel 600 / 625 / 718 | ASTM B564 | Heat exchangers, aerospace | |
| Incoloy 800 / 825 | ASTM B564 | Petrochemical & chemical processing | |
| Hastelloy C22 / C276 | ASTM B564 | Severe corrosion resistance | |
| Monel 400 / K500 | ASTM B564 | Seawater, marine engineering | |
| Alloy 20 | ASTM B564 | Sulfuric acid services | |
| Nimonic 75 / 80A | ASTM B564 / B637 | High-temp aerospace & turbines | |
| Copper Nickel | Cu-Ni 90/10 / 70/30 | ASTM B151 / B467 | Marine systems, seawater service |
| Titanium | Grade 2 / Grade 5 | ASTM B381 | Lightweight, corrosion resistance |
| Aluminium | 6061 / 5083 | ASTM B247 | Low-pressure, non-corrosive piping |
Explore Forged Fittings
- Forged Fitting
- Elbow (Threaded / Socket Weld)
- Tee (Threaded / Socket Weld)
- Union (Threaded / Socket Weld)
- Coupling (Threaded / Socket Weld)
- Plug (Threaded / Socket Weld)
- Bushing (Threaded / Socket Weld)
- Cap (Threaded / Socket Weld)
- Cross (Threaded / Socket Weld)
- Nipple (Threaded / Socket Weld)
- Forged Boss
- Forged Insert
- Swage Nipple
- Bull Plug
- Street Elbow
Request for an Immediate Offer?
We will reply you in 2 hours during support time!
Conctact Now!Explore All Products
Dimensions of ASME B16.11 Forged Insert (Class 2000#, 3000#, 6000#)
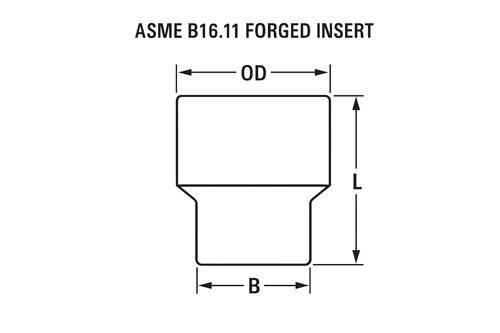
| Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) | Socket Bore (B) mm | Outside Diameter (OD) mm | Length (L) mm | Pressure Class (2000 / 3000 / 6000) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/8″ | 6.5 | 10 | 25 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 1/4″ | 9.5 | 14 | 28 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 3/8″ | 13.0 | 17 | 30 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 1/2″ | 16.0 | 21 | 32 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 3/4″ | 21.5 | 27 | 35 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 1″ | 27.0 | 34 | 38 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 1 1/4″ | 36.0 | 43 | 42 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 1 1/2″ | 41.0 | 49 | 45 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 2″ | 53.0 | 62 | 50 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 2 1/2″ | 64.0 | 75 | 55 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 3″ | 79.0 | 90 | 60 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 4″ | 105.0 | 115 | 65 | 2000 – 6000 |
Dimensions of ASME B16.11 Socket Weld Reducer Insert (Class 2000#, 3000#, 6000#)
| Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) | Larger Bore (B1) mm | Smaller Bore (B2) mm | Outside Diameter (OD) mm | Length (L) mm | Pressure Class (2000 / 3000 / 6000) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2″ × 1/4″ | 16.0 | 9.5 | 21 | 32 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 3/4″ × 1/2″ | 21.5 | 16.0 | 27 | 35 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 1″ × 1/2″ | 27.0 | 16.0 | 34 | 38 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 1″ × 3/4″ | 27.0 | 21.5 | 34 | 38 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 1 1/4″ × 1/2″ | 36.0 | 16.0 | 43 | 42 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 1 1/4″ × 3/4″ | 36.0 | 21.5 | 43 | 42 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 1 1/4″ × 1″ | 36.0 | 27.0 | 43 | 42 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 1 1/2″ × 1/2″ | 41.0 | 16.0 | 49 | 45 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 1 1/2″ × 3/4″ | 41.0 | 21.5 | 49 | 45 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 1 1/2″ × 1″ | 41.0 | 27.0 | 49 | 45 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 2″ × 1″ | 53.0 | 27.0 | 62 | 50 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 2″ × 1 1/2″ | 53.0 | 41.0 | 62 | 50 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 2 1/2″ × 2″ | 64.0 | 53.0 | 75 | 55 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 3″ × 2″ | 79.0 | 53.0 | 90 | 60 | 2000 – 6000 |
| 4″ × 3″ | 105.0 | 79.0 | 115 | 65 | 2000 – 6000 |
Weight Chart: ASME B16.11 Insert
| Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) | DN (mm) | 2000# (kg) | 3000# (kg) | 6000# (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/4″ | 8 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.06 |
| 3/8″ | 10 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.08 |
| 1/2″ | 15 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.11 |
| 3/4″ | 20 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.17 |
| 1″ | 25 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.24 |
| 1 1/4″ | 32 | 0.23 | 0.26 | 0.34 |
| 1 1/2″ | 40 | 0.29 | 0.32 | 0.42 |
| 2″ | 50 | 0.40 | 0.44 | 0.58 |
| 2 1/2″ | 65 | 0.52 | 0.58 | 0.76 |
| 3″ | 80 | 0.70 | 0.76 | 1.00 |
| 4″ | 100 | 1.05 | 1.15 | 1.50 |
Socket Weld Reducer Insert Tolerances as per ASME B16.11
| NPS | Socket Bore ±mm | OD ±mm | Length ±mm | Thread Length ±mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/8″ – 1/2″ | 0.2 | 0.3 | 1.5 | 0.2 |
| 3/4″ – 2″ | 0.25 | 0.3–0.5 | 2 | 0.3 |
| 2½” – 4″ | 0.3–0.5 | 0.5–0.8 | 2–3 | 0.5 |
| 5″ – 6″ | 0.5 | 0.8 | 3 | 0.5 |
How does a Socket Weld Reducer Insert differ from a Regular Socket Weld Insert?
-
Socket Weld Reducer Insert:
- Designed to connect pipes of different diameters.
- Wall thickness at the larger socket end is slightly increased to handle welding stresses and pressure differences.
- Provides a smooth internal bore transition, reducing turbulence in critical flow applications.
- Can be concentric or eccentric, depending on piping alignment requirements.
-
Regular Socket Weld Insert:
- Designed to connect pipes of the same diameter.
- Wall thickness is uniform along the insert.
- Provides reinforced connection for high-pressure or high-temperature piping but without diameter transition.
-
Key Advantage of Reducer Insert:
- Ensures structural integrity and smooth flow at diameter changes.
- Prevents stress concentration and erosion at joints where pipe diameters differ.
Are forged inserts suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications?
Yes, depending on material grade:
- Carbon Steel: Suitable for moderate temperature ranges.
- Alloy Steel: Can handle high-temperature pressure vessels.
- Stainless Steel (304, 316, 316L): Suitable for cryogenic and corrosive media.
What makes forged inserts more reliable than standard fittings?
- Single forged piece eliminates seams or welds prone to failure.
- Controlled machining tolerances ensure precise fit in sockets, preventing misalignment.
- Enhanced fatigue strength due to aligned grain flow.
- Minimizes erosion at high-velocity fluid junctions.
